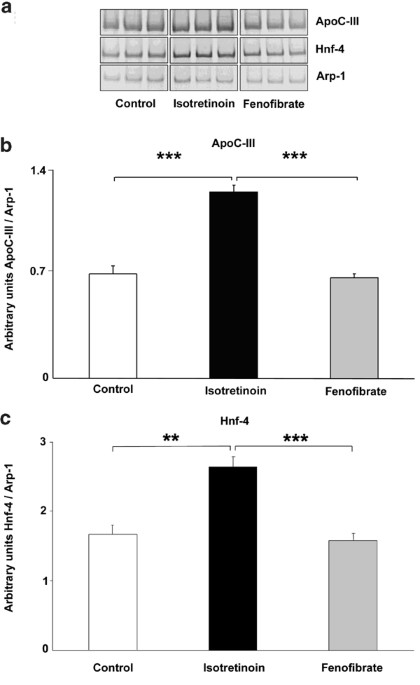
Hof1 plays a checkpoint-related role in MMS-induced DNA damage response in Candida albicans
4.5 (181) · € 21.00 · Auf Lager


Nucleotide Excision Repair Protein Rad23 Regulates Cell Virulence Independent of Rad4 in Candida albicans

Nucleotide Excision Repair Protein Rad23 Regulates Cell Virulence Independent of Rad4 in Candida albicans

Critical Role of DNA Checkpoints in Mediating Genotoxic-Stress–induced Filamentous Growth in Candida albicans

Nucleotide Excision Repair Protein Rad23 Regulates Cell Virulence Independent of Rad4 in Candida albicans

Nucleotide Excision Repair Protein Rad23 Regulates Cell Virulence Independent of Rad4 in Candida albicans
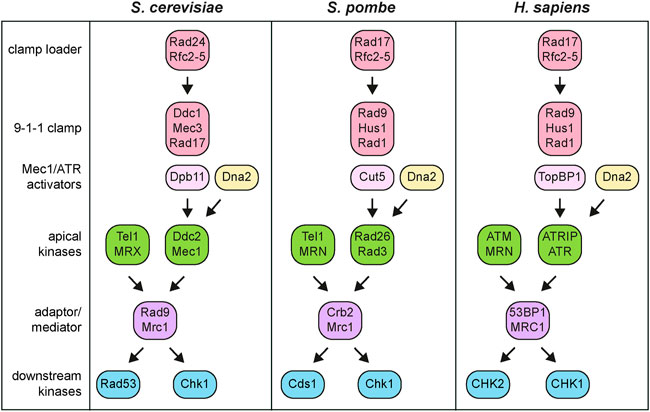
Frontiers The DNA damage checkpoint: A tale from budding yeast

Critical Role of DNA Checkpoints in Mediating Genotoxic-Stress–induced Filamentous Growth in Candida albicans
RAD23 deletion rescues hof1/hof1 MMS sensitivity. (A) The indicated

Molecular Microbiology, Microbiology Journal

GSTpi reduces DNA damage and cell death by regulating the ubiquitination and nuclear translocation of NBS1