RV increases the number and amplitude of Ca 2+ spikes at the
4.7 (585) · € 22.00 · Auf Lager


Activation State-Dependent Substrate Gating in Ca2+/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II

A stochastic model of hippocampal synaptic plasticity with geometrical readout of enzyme dynamics
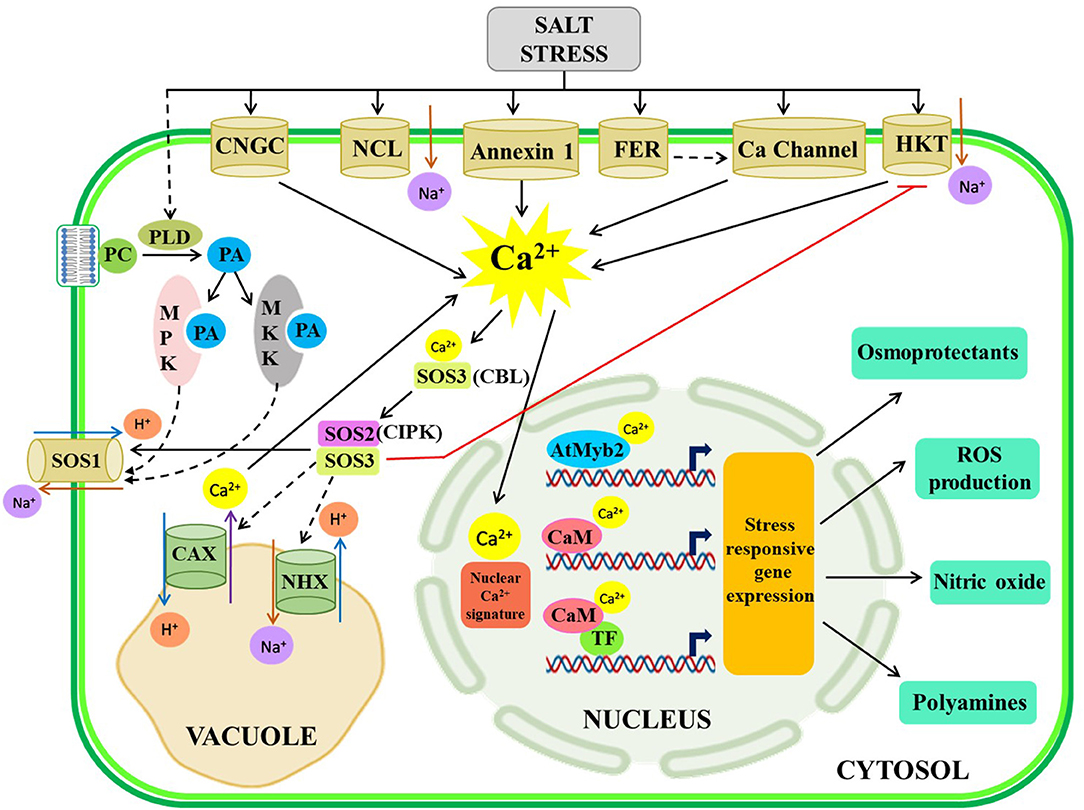
Frontiers TypiCal but DeliCate Ca++re: Dissecting the Essence of Calcium Signaling Network as a Robust Response Coordinator of Versatile Abiotic and Biotic Stimuli in Plants

IJMS, Free Full-Text

Synaptic memory and CaMKII
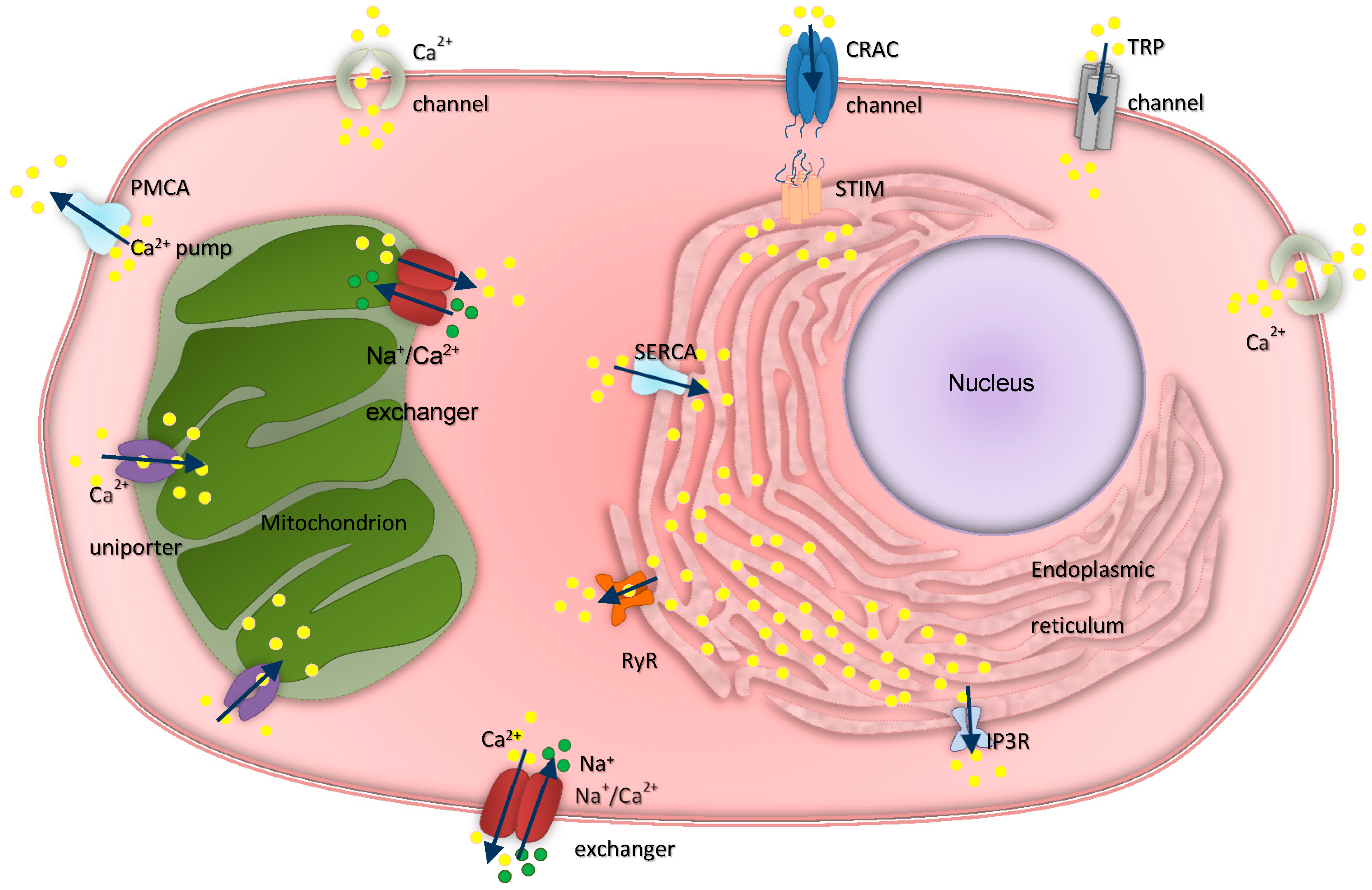
Cancers, Free Full-Text
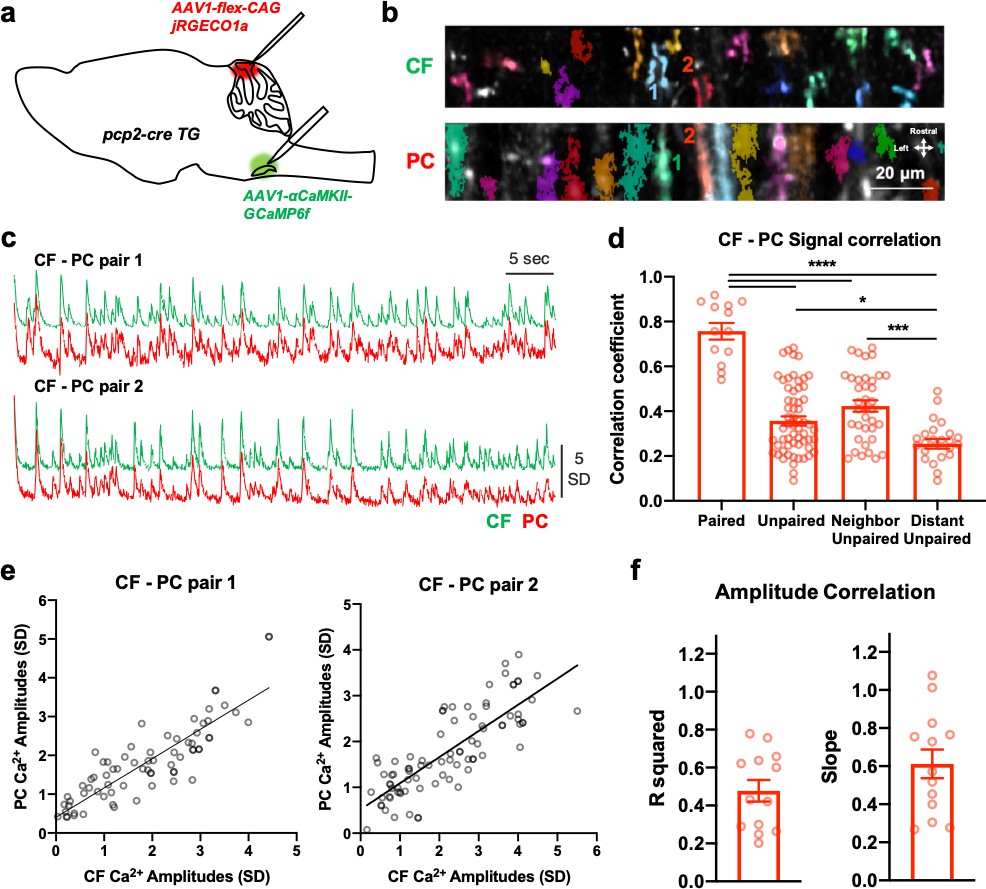
Direct translation of climbing fiber burst-mediated sensory coding into post-synaptic Purkinje cell dendritic calcium

Unusually Slow Spike Frequency Adaptation in Deep Cerebellar Nuclei Neurons Preserves Linear Transformations on the Subsecond Timescale

Dentate gyrus mossy cells exhibit sparse coding via adaptive spike threshold dynamics

Unusually Slow Spike Frequency Adaptation in Deep Cerebellar Nuclei Neurons Preserves Linear Transformations on the Subsecond Timescale